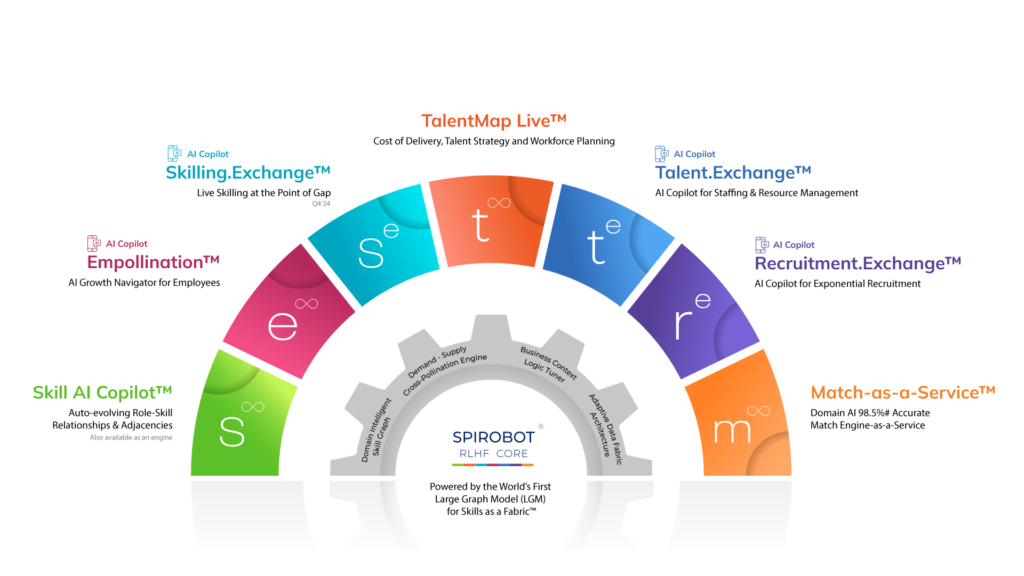
In today’s rapidly evolving business environment, the concept of a skills taxonomy has become a central theme in workforce development strategies. At its core, skills taxonomy is an organized classification system that helps categorize skills into a structured format. While this seems beneficial on the surface, it becomes evident that such a rigid system needs to address the dynamic needs of the modern workforce.
This blog explores the limitations of skills taxonomies and highlights the necessity for a more flexible and adaptive approach with auto-evolving role-skill frameworks.
What is a Skills Taxonomy?
A skills taxonomy is a structured classification of skills, typically hierarchically organized. It provides a standardized vocabulary for skills, making identifying and managing employee capabilities easier. For instance, in an IT organization, a skills taxonomy might categorize skills under broad categories like “Programming Languages” or “Project Management,” which are then further subdivided into specific skills like “Java,” “Python,” or “Agile Methodologies.”
While skills taxonomy offers a systematic way to categorize and evaluate skills, its static nature inherently limits it.
While skills taxonomy offers a systematic way to categorize and evaluate skills, it is inherently limited by its static nature. The modern workforce requires a dynamic approach that can adapt to the continuously evolving landscape of skills and roles.
Skill Taxonomy: The Need for Flexibility
The rigidity of a traditional skill taxonomy becomes a significant hindrance when considering the fast-paced changes in industry requirements and technological advancements. Once defined, a skill taxonomy often remains static until manually updated. This lag can result in outdated skill profiles, misaligned training programs, and a workforce unprepared for new challenges.
A skill taxonomy remains static until manually updated.
This lag can result in outdated skill profiles, misaligned training programs, and a workforce unprepared for new challenges.
Moreover, the static nature of skills taxonomy fails to capture the nuanced and often interdisciplinary nature of many modern roles. For instance, a data scientist today needs to possess a blend of skills in statistics, programming, domain knowledge, and communication. A traditional skill taxonomy may categorize these skills separately, failing to recognize these roles’ interconnectedness and evolving nature.
Ontology vs. Taxonomy: A Comparative Insight
To understand the limitations of skills taxonomy, it’s essential to compare it with ontology. In this context, skills ontology refers to a more dynamic and interconnected framework that not only categorizes skills but also defines the relationships between them. While a skills taxonomy might list “Java” and “Python” as separate entities under “Programming Languages,” an ontology would establish relationships showing how expertise in “Java” can complement skills in “Spring Framework” or “Microservices Architecture.”
This relational approach offered by ontology is crucial for modern workforce management, as it provides a more holistic view of an individual’s capabilities and how they can be applied across various roles and projects. Ontologies can evolve, incorporating new skills and relationships as they emerge, which is a significant advantage over the static nature of taxonomies. However, they are still incapable of handling an evolved workforce’s role and skill relationships.
The Skills Taxonomy Trap – Drawbacks of Skills Taxonomy
The primary limitation of skills taxonomy lies in its inherent rigidity and inability to adapt quickly to changing industry needs. This static approach can lead to several issues:
Drawbacks of Skills Taxonomy
– Outdated Skill Profiles
– Misaligned Training Programs
– Inefficient Talent Management
– Reduced Employee Engagement
- Outdated Skill Profiles: As industry requirements evolve, a static skills taxonomy fails to keep pace, resulting in obsolete skill profiles that do not reflect current market demands.
- Misaligned Training Programs: Training programs based on an outdated skills taxonomy may not equip employees with the necessary skills for emerging roles, leading to a skills gap.
- Inefficient Talent Management: With a dynamic system to capture evolving skill sets, organizations may be able to effectively manage and deploy talent, but this can lead to inefficiencies and missed opportunities.
- Reduced Employee Engagement: Employees may feel undervalued if their evolving skill sets are not recognized and utilized, leading to reduced engagement and retention.
Introducing Auto-Evolving Role-Skill Frameworks
There is a growing need for auto-evolving role-skill frameworks to address the limitations of traditional skills taxonomy. These frameworks leverage advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and large graph models, to create dynamic, interconnected, and continually updating skill profiles. Auto-evolving role-skill frameworks significantly evolve how organizations manage and develop their workforce.
The Need for Dynamic Skill Management
In a world of accelerating technological change and industry evolution, more than a static approach to skills management is required. Auto-evolving role-skill frameworks provide a solution that adapts in real time, ensuring that organizations can keep up with the rapid changes in required competencies. These frameworks continuously update skill profiles based on emerging trends, new technologies, and evolving industry standards, providing a more accurate and relevant view of an organization’s capabilities.
How Auto-Evolving Frameworks Work
Auto-evolving role-skill frameworks utilize sophisticated algorithms and large graph models to analyze vast amounts of data from various sources. These sources include job postings, industry reports, employee performance data, and more. By processing this information, the frameworks can identify new skills gaining importance, recognize patterns in skill development, and anticipate future skill needs.
For example, if a new programming language becomes popular in the tech industry, an auto-evolving framework can quickly identify this trend and update the relevant skill profiles. This ensures that the organization knows the new skill requirement and can proactively train employees or hire new talent with the necessary expertise.
Benefits of Auto-Evolving Role-Skill Frameworks
Benefits of Auto-Evolving Role-Skill Frameworks
– Real-Time Adaptation
– Interconnected Skill Mapping
– Proactive Workforce Planning
– Enhanced Employee Development
– Improved Recruitment Strategies
– Efficient Talent Management
– Integration with Existing Systems
- Real-Time Adaptation: One of the most significant advantages of auto-evolving role-skill frameworks is their ability to adapt in real time. As new and existing skills emerge, the framework updates accordingly, providing a current and accurate representation of the organization’s skill set.
- Interconnected Skill Mapping: Unlike traditional skills taxonomy, which often treats skills as isolated entities, auto-evolving frameworks recognize the relationships between skills. This interconnected mapping helps us understand how different skills complement each other and how they can be combined to meet complex job requirements.
- Proactive Workforce Planning: With an up-to-date view of the skills landscape, organizations can engage in more effective workforce planning. They can identify potential skill gaps before they become critical, allowing for timely training and development initiatives. This proactive approach ensures that the organization remains competitive and prepared for future challenges.
- Enhanced Employee Development: Auto-evolving frameworks provide employees with clear and relevant career development paths. Employees know what skills they need to develop by continuously updating skill requirements to advance in their careers. This transparency fosters a culture of continuous learning and growth.
- Improved Recruitment Strategies: Accurate and current understanding of required skills is crucial when hiring new talent. Auto-evolving frameworks enable organizations to refine their recruitment strategies, ensuring job postings accurately reflect the skills needed for success. This leads to better hiring decisions and a more capable workforce.
- Efficient Talent Management: Managing talent effectively requires an in-depth understanding of employees’ skills and how they align with organizational needs. Auto-evolving frameworks provide this insight, enabling better talent allocation, performance evaluation, and succession planning.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Auto-evolving frameworks are designed to integrate seamlessly with existing talent management systems. This ensures that the benefits of dynamic skill management are realized across all human resources aspects, from recruitment to training and performance management.
Spire.AI: Revolutionizing Role-Skill Frameworks
The primary limitation of skills taxonomy lies in its inherent rigidity and inability to adapt quickly to changing industry needs. This static approach can lead to several issues:
The shift towards auto-evolving role-skill frameworks marks a significant advancement in workforce management.
By moving beyond the limitations of traditional skills taxonomy, organizations can better prepare for the future, ensuring their workforce is equipped with the skills needed to thrive in a rapidly changing environment.
The Key Benefits of Spire.AI’s Framework
- Dynamic and Adaptive: Unlike static taxonomies, Spire.AI’s framework evolves quickly, adapting to new skills and changing industry demands.
- Comprehensive Skill Mapping: The LGM-based framework captures intricate relationships between skills, providing a holistic view of an individual’s capabilities.
- Ready to Deploy: The framework is pre-configured and easily customizable to fit any business context, ensuring quick implementation and immediate benefits.
- Single Source of Truth: It is an auto-evolving source of truth for skills and roles data, seamlessly integrating with existing talent systems and processes.
- Enhanced Talent Management: The framework enables more effective talent management, from recruitment to training and development, by providing accurate and up-to-date skill profiles.
- Increased Employee Engagement: Recognizing and utilizing employees’ evolving skill sets leads to higher engagement and retention rates.
The Future of Workforce Management
The future of workforce management hinges on several key factors emphasizing flexibility, adaptability, and continuous learning. Here are some critical aspects that organizations need to consider:
Embracing Continuous Learning
In the modern workplace, lifelong learning has become essential. With the pace of technological advancements and industry changes, employees must continuously update their skills. Auto-evolving role-skill frameworks support this by identifying skill gaps and recommending targeted training programs. This approach ensures employees always learn and adapt, making the organization more resilient to change.
Leveraging Advanced Technologies
Technologies such as artificial intelligence and domain-intelligent solutions are revolutionizing how organizations manage their workforce. These technologies enable the creation of dynamic skill profiles that evolve based on real-time data. For instance, AI can automatically analyze job market trends, employee performance, and emerging skills to update role requirements automatically. This ensures the organization remains competitive and quickly adapts to new industry standards.
Enhancing Employee Engagement
A dynamic and responsive approach to skills management significantly enhances employee engagement. When employees see their skills are recognized and valued, they are more likely to feel motivated and committed to their roles. Auto-evolving frameworks ensure that employees’ evolving capabilities are continuously integrated into their career development plans, fostering a culture of growth and innovation.
Improving Talent Mobility
One significant benefit of a flexible skills management approach is improved talent mobility within the organization. By having an up-to-date and comprehensive view of employees’ skills, organizations can more effectively match employees to new roles and projects. This optimizes talent utilization and provides employees with opportunities for career advancement and personal development.
Facilitating Better Decision-Making
Auto-evolving role-skill frameworks provide managers with accurate and up-to-date information about the skills landscape within the organization. This data-driven approach enables better hiring, training, and workforce planning decisions. Managers can identify emerging skills critical to the business and ensure the organization is prepared to meet future demands.
Supporting Diversity and Inclusion
Dynamic skills frameworks can also play a crucial role in promoting diversity and inclusion in the workplace. By focusing on skills rather than traditional qualifications or backgrounds, organizations can identify and nurture talent from diverse sources. This approach helps build a more inclusive workforce that brings varied perspectives and innovative ideas to the table.
Adapting to Remote and Hybrid Work Models
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the shift towards remote and hybrid work models. These new work arrangements require different skills, including digital literacy, self-management, and virtual collaboration. Auto-evolving frameworks can quickly adapt to these changes, ensuring employees have the skills to succeed in remote and hybrid environments.
Reducing Skill Redundancy
In a static skills taxonomy, there is often a risk of skill redundancy, where specific skills become obsolete over time but remain part of the defined framework. This can lead to inefficiencies and wasted resources. An auto-evolving framework continuously updates skill requirements based on current and future needs, minimizing redundancy and ensuring that training and development efforts are focused on relevant skills.
Conclusion
The future of workforce management lies in continually adapting and evolving, ensuring that employees’ skills are always aligned with industry needs. The limitations of traditional skills taxonomy are becoming increasingly apparent, making it essential for organizations to adopt more flexible and adaptive frameworks. Auto-evolving role-skill frameworks, such as those offered by Spire.AI, provide a comprehensive solution that addresses these challenges.
Organizations can create a more agile and responsive workforce by leveraging advanced technologies, fostering continuous learning, and enhancing employee engagement. This dynamic approach to skills management prepares the organization for future challenges and ensures that employees feel valued and motivated in their roles.
Spire.AI’s innovative framework represents a significant step forward in workforce management, providing organizations with the tools they need to succeed in an ever-changing world. As the business landscape continues to evolve, the ability to adapt and grow will be the defining factor in achieving long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to create a skill taxonomy?
To create a skill taxonomy, identify core skills, categorize them into hierarchical levels, define skill descriptions, and ensure consistency and clarity.
What is skills taxonomy hierarchy?
A skills taxonomy hierarchy is a structured arrangement of skills from broad categories to specific subcategories, creating a clear classification system.
What is the difference between skills ontology and skills taxonomy?
A skills taxonomy is a hierarchical classification of skills, while an ontology adds relationships and definitions to create a more complex understanding.