In the realm of talent management, data is a crucial asset. It informs stakeholders about decisions, shapes strategies, and ultimately drives the success of organizations. However, when talent data is deficient, the ramifications can be significant.
This blog delves into what talent data deficiency is, its root causes, and the consequential impact on decision-making and operational efficiency in talent management.
What is Talent Data Deficiency?
Imagine a car without fuel. It might be sleek and well-designed, but it can’t take you anywhere. Talent data deficiency is similar. Talent data deficiency refers to the situation where there is an insufficient amount of relevant, accurate, and accessible data regarding an organization’s workforce. This can manifest in several ways:
- Incomplete Data: Missing critical information about employees’ skills, experiences, and performance.
- Outdated Data: Information that is no longer relevant or accurate because it hasn’t been updated regularly.
- Inaccessible Data: Data that is siloed in different systems making it difficult to obtain a comprehensive view.
Causes of Talent Data Deficiency
Several factors contribute to talent data and employee data deficiency. Understanding these causes is the first step toward addressing the issue.
Causes of Talent Data Deficiency
1. Lack of Data Collection Mechanisms
2. Siloed Data Systems
3. Outdated Data
4. Poor Data Quality
5. Insufficient Data Integration
1. Lack of Data Collection Mechanisms
Organizations often fail to implement robust data collection mechanisms. This could be due to a lack of awareness about the importance of data, insufficient technological tools, or simply poor data management practices. Without systematic data collection, organizations miss valuable insights into their workforce.
2. Siloed Data Systems
In many organizations, data is stored in disparate systems that do not communicate with each other. This fragmentation creates isolated pockets of information, preventing a holistic view of the talent landscape. For instance, data from HR systems, performance management tools, and learning and development platforms may not be integrated.
3. Outdated Data
Data that is not regularly updated quickly becomes irrelevant. Employee skills, experiences, and career aspirations evolve; data systems must reflect these changes. Outdated data can lead to incorrect assumptions and decisions, hindering effective talent management.
4. Poor Data Quality
Inaccurate, inconsistent, or duplicated data can severely impair the quality of insights generated. Poor data quality can arise from errors in data entry, lack of standardization in data formats, and insufficient validation processes.
5. Insufficient Data Integration
The inability to integrate data from multiple sources limits its usefulness even when data is collected and stored. Integration is crucial for creating a comprehensive and actionable view of talent data, allowing for better analysis and decision-making.
Impact of Talent Data Deficiency
The impact of talent data deficiency is far-reaching, affecting various aspects of talent management and overall organizational performance.
Impact of Talent Data Deficiency
1. Inadequate Talent Insights
2. Poor Decision-Making
3. Reduced Operational Efficiency
4. Limited Predictive Analytics
1. Inadequate Talent Insights
Organizations struggle to gain meaningful insights into their workforce without sufficient and accurate data. This lack of understanding hampers the ability to identify skill gaps, assess employee performance, and plan for future talent needs.
2. Poor Decision-Making
Decision-making in talent management relies heavily on data-driven insights. When the data is incomplete or outdated, recruitment, development, and retention decisions are based on flawed assumptions. This can lead to ineffective strategies and missed opportunities.
3. Reduced Operational Efficiency
Operational processes in talent management, such as recruitment, onboarding, and succession planning, become more efficient with reliable data. For example, recruiting the right candidates becomes challenging when there is no clear understanding of the skills and competencies required for specific roles.
4. Limited Predictive Analytics
Advanced analytics and AI rely on robust data to predict trends and outcomes. Talent data deficiency limits the ability to leverage these technologies effectively. As a result, organizations need to take advantage of the benefits of predictive analytics in areas such as workforce planning and employee development.
Addressing Talent Data Deficiency
Tips to Overcome Talent Data Deficiency
– Implement Robust Data Collection Methods
– Ensure Data Integration Across Systems
– Regularly Update and Maintain Data Quality
– Leverage AI and Machine Learning
Addressing talent data deficiency requires a multi-faceted approach that improves data collection, integration, and quality. Here are some strategies:
1. Implement Robust Data Collection Methods
Organizations must establish comprehensive data collection mechanisms that capture relevant information about employees. This includes implementing tools and processes that facilitate regular data updates and ensure accuracy.
2. Ensure Data Integration Across Systems
Integrating data from various systems is crucial for creating a unified view of the talent landscape. Organizations should invest in technologies and platforms that enable seamless data integration and eliminate silos.
3. Regularly Update and Maintain Data Quality
Data maintenance should be an ongoing process. Regular audits, data cleaning, and validation are essential to ensure the data remains accurate and relevant. Implementing data governance frameworks can help in maintaining high data quality standards.
4. Leverage AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning technologies can enhance data insights and predict future trends. These technologies can analyze large volumes of data, identify patterns, and provide actionable recommendations. Organizations should explore AI-driven solutions to optimize talent management processes.
Spire.AI: The Best Solution for Talent Operations
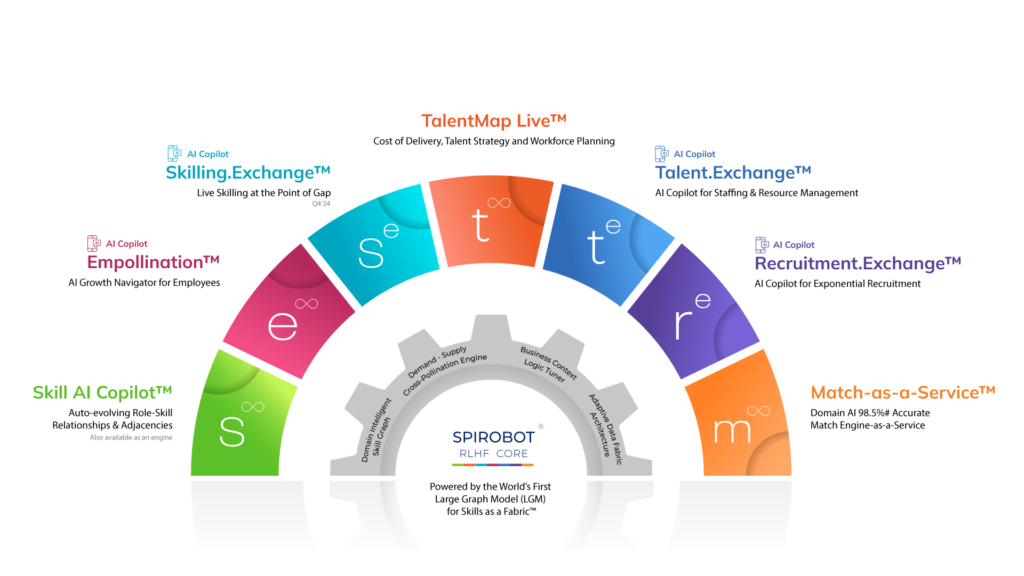
To effectively address talent data deficiency, organizations can turn to advanced solutions like Spire.AI.
Spire.AI is an AI Copilot for Talent that supports the evolving talent operating model requirements of future-ready companies transforming into Skills-Based Organizations (SBO).
Auto-Evolving Role-Skill Framework
Spire.AI’s auto-evolving domain-intelligent Large Graph Model (LGM)-based Role-Skill Framework identifies complex skill mixes and requirements for every role at the base, enhanced, and expert levels. This framework is a single source of truth for skills and roles data, making it easily deployable across talent systems and processes.
Data Aggregation with Skill Profiles
Spire.AI generates automatic AI-generated employee skill profiles by aggregating and understanding unstructured data from various sources. This results in comprehensive skill profiles for about 83% of the employee base with minimal input.
Spire.AI auto-generates comprehensive skill profiles for about 83% of the employee base with minimal input.
Career Path Simulation and Reskilling Recommendations
Spire.AI provides precise recommendations for upskilling, reskilling, and career growth, aligning employees’ aspirations with the organization’s strategic direction.
Talent Marketplace
Spire.AI’s talent marketplace empowers employees with internal mobility opportunities, ensuring a democratic environment for growth while maintaining governance through Business Context Logic (BCL).
Talent Acquisition
Spire.AI reduces the cost per hire by up to 70% and ensures that up to 90% of talent demands are met on any given day, significantly improving recruitment efficiency and effectiveness.
Spire.AI reduces the cost per hire by up to 70% and ensures that up to 90% of talent demands are met on any given day
Resource Management
Spire.AI optimizes the forecast-to-fulfill operating model for professional services, impacting operating margins positively.
Real Business Impact
Spire.AI has demonstrated significant business impacts, such as reducing IT costs, increasing internal mobility, and transforming organizations into skills-based entities.
For example, a global communications leader experienced a 20% IT cost reduction and increased internal mobility from 21% to 56% within eight weeks of implementation.
Conclusion
Talent data deficiency poses a significant challenge to effective talent management. By understanding its causes and impacts, organizations can take proactive steps to address the issue. Leveraging advanced solutions like Spire.AI can transform talent operations, enabling better decision-making, improved operational efficiency, and ultimately driving business success. Embracing comprehensive data management and innovative technologies is key to overcoming talent data deficiency and unlocking the full potential of an organization’s workforce.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is talent data important?
Talent data is crucial for making informed decisions about workforce planning, talent acquisition, development, and retention. It provides insights into employee performance, skills, and potential.