Organizations are increasingly moving away from traditional job-based hierarchies and embracing skills-based models to stay agile and relevant. To pivot towards these models, they need tools to manage talent in a dynamic environment. At the core of this transformation lies an evolving skills graph—a system that maps the interconnectedness of skills, roles, and workforce needs in real-time.
A skills graph is not just a static repository but an adaptive framework that updates skill adjacencies, trends, and role requirements as industries evolve. This evolving structure empowers organizations to manage talent precisely, enhancing productivity, employee engagement, and long-term business success. This article will explore how skills graphs drive talent management transformation and enable organizations to thrive in a skills-based operating model.
What is a Skills Graph?
A skills graph is an advanced framework that dynamically maps the relationships between various skills, competencies, and job roles. Think of it as a living database that connects individual skills and their adjacencies, contextual relevance, and demand in real-time across industries. Unlike traditional static skills matrices, the evolving skills graph updates continuously based on internal workforce changes and external market trends.
A skills graph is an advanced framework that dynamically maps the relationships between various skills, competencies, and job roles.
For example:
- It highlights skill adjacencies (i.e., transferable skills) that enable employees to shift roles seamlessly.
- It identifies emerging skills in response to market changes, aligning training and hiring efforts with future needs.
- It tracks employee development paths, automatically suggesting reskilling or upskilling based on individual goals and company needs.
Organizations can use a skills graph to map employees’ skills to evolving business goals, making workforce planning highly efficient and forward-looking.
Why Skills-Based Organizations Need an Evolving Skills Graph
A skills-based organization (SBO) shifts focus from rigid roles and job descriptions to a more fluid structure where skills, not positions, drive operations. This shift offers many benefits:
- Enhanced Workforce Agility: Employees can pivot across roles based on transferable skills.
- Optimized Talent Utilization: Companies can efficiently redeploy talent internally to meet changing project demands.
- Reduced Hiring Costs: By reskilling employees rather than hiring externally, organizations can address skill gaps faster and cost-effectively.
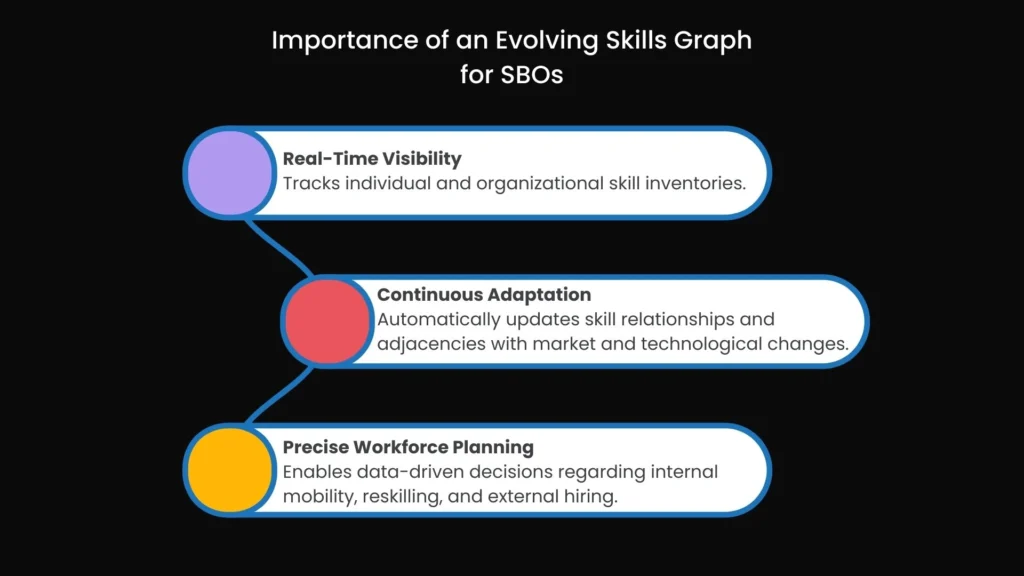
An evolving skills graph is essential for SBOs because it offers:
- Real-Time Visibility: Tracks individual and organizational skill inventories.
- Continuous Adaptation: Automatically updates skill relationships and adjacencies with market and technological changes.
- Precise Workforce Planning: Enables data-driven decisions regarding internal mobility, reskilling, and external hiring.
According to research, 44% of the core skills required for jobs today will change within the next 3 years. Organizations with an evolving skills graph will be better positioned to manage talent effectively as these shifts occur.
The Role of the Skills Graph in Workforce Planning and Career Development
The evolving skills graph is critical in optimizing workforce planning, development, and employee engagement. Its ability to provide real-time, data-driven insights into workforce capabilities allows organizations to precisely plan for current and future needs. Below are key ways the skills graph contributes to effective workforce planning and career development.
1. Comprehensive Skill Mapping and Employee Profiling
The first step in workforce planning is understanding the current talent landscape. A skills graph’s primary strength is tracking technical and functional competencies, focusing on measurable and relevant abilities required to fulfill specific roles. Unlike traditional static systems that rely on general job descriptions, a skills graph focuses on role-specific, technical proficiencies and industry-aligned skills, ensuring precision in workforce planning.
- Role-Centric Technical Skills: The graph captures the critical technical abilities associated with each role, enabling a clear view of the organization’s current capabilities and skill gaps.
- Adjacent and Emerging Skill Insights: Beyond primary skills, the graph identifies adjacent technical skills—transferable or complementary to an employee’s current expertise—that allow for smooth transitions across roles or functions.
This complete visibility into workforce capabilities ensures that organizations can accurately plan talent deployment and development, reducing skill gaps and bottlenecks.
2. Identifying Skill Gaps and Designing Reskilling Programs
An essential feature of the skills graph is its ability to conduct real-time skill gap analyses. New skills become critical as the business landscape evolves, and existing ones may lose relevance. The skills graph identifies these gaps at both an organizational and individual level, enabling the design of targeted learning programs.
- Role-Based Skill Gap Analysis: The graph compares the skills required for specific roles against employees’ current skills, pinpointing gaps that must be addressed.
- Tailored Reskilling Plans: Employees receive personalized recommendations to fill these gaps, including formal training, certifications, or hands-on project experience.
This proactive approach ensures employees develop relevant skills, keeping the organization agile and ready for future challenges.
3. Demand-Supply Matching and Optimized Talent Deployment
One of the biggest challenges in workforce management is ensuring that the right people are assigned to the right roles at the right time. The skills graph is crucial in demand-supply matching, mapping available skills to project needs and business demands.
- Real-Time Talent Deployment: The graph dynamically aligns employees with projects based on skill requirements, ensuring optimal talent utilization.
- Cross-Functional Matching: It can also suggest employees with adjacent skills who can transition into high-demand roles, enhancing workforce flexibility.
By efficiently matching internal talent with business needs, organizations can reduce dependency on external hiring, shorten time to fill critical roles, and minimize downtime.
4. Career Path Development and Internal Mobility
The skills graph encourages internal mobility by identifying potential career paths within the organization. Employees benefit from visibility into vertical and lateral career opportunities, fostering a sense of progression and engagement.
- Visualizing Career Paths: Employees can explore future roles based on their current skill set and the skills they need to acquire for advancement. This transparency motivates employees to take ownership of their professional growth.
- Seamless Transitions Across Roles: The graph identifies adjacent skills that make it easier for employees to transition into new roles, promoting career development without requiring extensive retraining.
This fluidity enhances job satisfaction and reduces turnover, as employees can grow within the organization rather than seeking opportunities elsewhere.
5. Capacity Planning for Future Workforce Needs
Workforce planning involves meeting today’s needs and preparing for future challenges. A skills graph supports capacity planning by offering insights into emerging skills and potential workforce shortages.
- Scenario Planning: HR teams can model different scenarios—such as new product launches or expansions—and assess whether the existing workforce can meet the anticipated demand.
- Proactive Skill Development: If gaps are identified, the organization can initiate reskilling and upskilling programs or start hiring efforts well in advance, ensuring smooth operations.
This capability allows organizations to stay ahead of industry trends, ensuring that they are never caught off guard by shifts in demand.
6. Fostering Employee Engagement Through Personalized Development
The organization’s ability to learn and grow is a crucial driver of employee engagement. The skills graph supports personalized development plans aligning with employee aspirations and business needs.
- Individual Learning Paths: Employees receive recommendations for courses, certifications, or mentoring opportunities that match their career goals and skill gaps.
- Transparent Opportunity Marketplace: The graph powers internal talent marketplaces, where employees can explore new roles and projects and apply for positions that align with their skills and interests.
Organizations foster a culture of continuous learning and engagement by empowering employees with visibility into growth opportunities and a clear path for development.
7. Agility and Workforce Resilience
The evolving nature of a skills graph makes it an essential tool for workforce agility and resilience. The ability to pivot quickly is crucial in rapid change, such as technological disruptions or economic shifts.
- Real-Time Adjustments: As new skills become critical, the graph identifies employees who can be trained quickly to meet emerging needs.
- Resilience Through Upskilling: The graph encourages upskilling by identifying skill adjacencies, ensuring the workforce remains adaptable to change.
This agility reduces the risks of sudden disruptions and ensures the organization can continue operating smoothly, even under challenging circumstances.
Spire.AI: A Pioneering Platform in Skills Graph Implementation
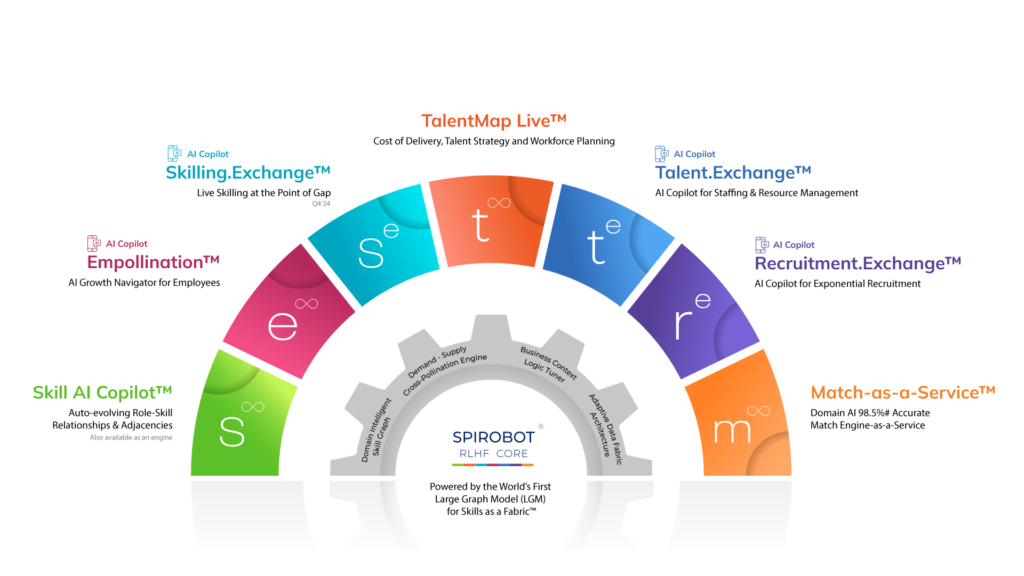
Spire.AI leads the way in skills graph implementation with its Domain-Intelligent AI platform, designed to transform organizations into adaptive, skills-based operations. Its Large Graph Model (LGM) for Skills is at the heart of this transformation, continuously mapping and updating relationships between 125,000 primary skills and 10.2 million interconnected nodes across 26 industries.
The Large Graph Model (LGM): Enabling Precision and Agility
The Spire.AI Large Graph Model (LGM) for Skills is the foundation for real-time skill mapping. Unlike traditional static skill matrices, the LGM for Skills evolves continuously to reflect market changes, technology trends, and internal workforce dynamics.
- Dynamic Skill Relationships and Adjacencies: The LGM captures nuanced skill connections, identifying complementary and adjacent skills, which allows employees to transition seamlessly between roles.
- Real-Time Skill Inventories: Organizations gain access to a comprehensive, up-to-date view of their internal talent pool, enabling them to make data-driven decisions regarding staffing, reskilling, and succession planning.
The LGM for Skill’s ability to update automatically ensures that organizations are always ready to respond to emerging business demands and skill requirements without relying on manual interventions.
Auto-Evolving Role-Skill Framework: Aligning Workforce Capabilities with Business Needs
Spire.AI’s auto-evolving role-skill framework ensures continuous alignment between employee skills and evolving roles. This framework dynamically adjusts role definitions and skill requirements based on industry trends and organizational priorities.
- Automated Role Definition Updates: As new skills emerge, the system automatically integrates them into existing role frameworks, ensuring relevance without manual reconfiguration.
- Single Source of Truth: The framework eliminates discrepancies across HR systems by providing a unified, consistent role-skill database, which powers workforce planning, learning, and performance management.
This auto-evolving structure is unique to the organization and ensures that employees remain equipped with relevant skills and that the organization can pivot swiftly to meet new challenges.
Precision Talent Matching and Proactive Workforce Optimization
Spire.AI’s platform matches internal talent to open roles and project demands using real-time skills data. The Match Engine-as-a-Service™ ensures high match accuracy by analyzing skill proficiency, recency, adjacencies, and business context.
- Demand-Supply Synchronization: Organizations can fill roles quickly by leveraging real-time insights into internal skill availability, reducing dependency on external hiring.
- Cross-Functional Mobility: The system identifies employees with transferable skills, enabling lateral movements and fostering cross-functional collaboration.
Optimized workforce utilization, minimal bench time, and a reduced need for external hiring create a lean, efficient talent management process.
Empowering Career Development through Personalized Learning Paths
Spire.AI’s platform enhances employee engagement by enabling personalized career development. Based on their current skill profiles, employees can explore lateral and vertical career paths, with real-time recommendations on the steps needed to progress.
- Learning at the Point of Gap: Employees receive actionable learning suggestions directly related to skill gaps in their target roles, streamlining reskilling efforts.
- Transparent Career Opportunities: Through internal talent marketplaces, employees can view open roles and projects that match their interests and skills, fostering a culture of internal mobility and continuous growth.
This focus on career development improves retention and ensures that the workforce remains future-ready and aligned with evolving organizational needs.
Final Thoughts: Leading with Skills to Shape the Future
The journey to becoming a skills-based organization is both exciting and challenging. It requires organizations to rethink traditional structures, invest in technology, and foster a culture of continuous growth. Those who embrace the evolving skills graph will lead the future—not by reacting to change but by anticipating it, adapting to it, and thriving in it.
In this new world of work, skills become the building blocks of innovation and growth. Organizations that harness the potential of their people through transparent, data-driven, and adaptive talent management will create lasting value—for employees, customers, and society at large.
With every skill mapped, developed, and applied, organizations and their people take one step closer to realizing their full potential—building a future where work is meaningful, growth is limitless, and success is shared.