In today’s dynamic job market, skills are the new currency. Companies constantly seek individuals with the right skillsets to stay ahead of the curve, leading to a surge in HR technologies designed to bridge the talent gap.
In the world of HR technology, a new buzzword has emerged: Large Graph Models (LGMs). Touted for their ability to revolutionize skills assessment and talent management, LGMs can feel like a complex black box for those unfamiliar with the underlying technology.
This blog post aims to demystify the “black box” of LGM and provide a beginner-friendly explanation of how they power skill-based talent management solutions..
What are Large Graph Models (LGMs)?
A Large Graph Model (LGM) is a powerful AI tool that excels at understanding relationships between different pieces of information.
Imagine a vast network of interconnected nodes, each representing a concept. This network could contain information about skills, jobs, educational programs, certifications, and individual profiles. LGMs excel at processing interconnected data, also known as graphs. They can learn complex patterns and make predictions by analyzing the relationships between these nodes.
Here’s how it translates to the world of skills:
- Nodes: These represent individual skills (e.g., Python programming, data analysis, content writing, social media marketing).
- Edges: The connections between nodes depict relationships between skills. Edges can indicate prerequisites (e.g., basic math skills are needed before learning advanced statistics), complementary skills (e.g., project management skills often work well with communication skills), or similar skill sets (e.g., both Java and C++ are programming languages).
Here’s an analogy to understand LGM better:
Think of a social network like Facebook. Users (nodes) are connected by friendships (edges). An LGM analyzing this network could learn exciting things – for example, people with similar educational backgrounds tend to communicate with each other. This knowledge can be used to recommend new connections or even predict future friendships.
LGM can analyze vast amounts of data to understand the relationships between different skills. They can learn which skills are often used together, which are prerequisites for others, and how they evolve over time.
In the context of skills, LGMs can analyze vast amounts of data to understand the relationships between different skills. They can learn which skills are often used together, which are prerequisites for others, and how they evolve. This knowledge is then used to power various applications in talent management.
How Does an LGM Learn?
LGMs are data-hungry beasts. Their ability to learn and make connections hinges on the quality and quantity of data they are fed. This data can come from various sources:
- Job descriptions: Analyzing job postings allows the LGM to understand the specific skills required for different roles.
- Employee profiles: Employee profiles containing skills, experience, and educational background provide valuable insights into the organization’s skill landscape.
- Learning content: Training materials, course descriptions, and learning pathways can reveal how skills are developed and interconnected.
- Industry trends: External data on in-demand skills and emerging technologies helps the LGM stay current with market needs.
By ingesting this vast amount of information, the LGM progressively builds its knowledge graph, continuously refining its understanding of the complex relationships between skills.
LGMs vs. Traditional Methods: Why Large Graph Models Are the Future of Skills Management
The talent landscape is constantly evolving. New skills emerge, industry demands shift, and companies need to ensure their workforce possesses the skills to stay ahead. Traditional methods of skills management, however, are struggling to keep pace.
The Shortcomings of Traditional Skills Management
Many companies rely on spreadsheets, HR software, or a combination of both to track employee skills. While these methods offer a basic level of organization, they fall short in several key areas:
Limited Connectivity: Traditional methods treat skills as isolated entities. They fail to capture the relationships between different skills, making it difficult to identify skill gaps or recommend complementary learning paths.
Data Silos: Skills information often resides in disparate systems, creating data silos that hinder a holistic view of an employee’s skill set and the company’s overall talent pool.
–> Limited Connectivity
–> Data Silos
–> Inflexibility
–> Limited Insights
Inflexibility: Traditional methods struggle to adapt to the dynamic nature of skills. New skills emerge constantly, and existing skill sets evolve over time. These systems lack the agility to keep pace with these changes.
Limited Insights: Traditional methods offer minimal analytical capabilities. They struggle to provide insights into critical trends, such as skill shortages or the effectiveness of training programs.
These limitations can significantly impact a company’s ability to thrive in today’s competitive environment. Companies struggle to make informed decisions about talent development, resource allocation, and hiring strategies without a clear understanding of their workforce’s skills.
Large Graph Models: A Paradigm Shift
LGMs represent a revolutionary approach to skills management. Unlike traditional methods, LGMs leverage the power of artificial intelligence (AI) to create a comprehensive map of skills and their relationships. This map, known as a skills graph, connects skills to related concepts like job roles, educational programs, and industry trends.
Here’s how LGM address the limitations of traditional methods
Connected Intelligence: LGMs capture the intricate relationships between skills. This allows for identifying skill clusters, potential skill gaps, and complementary learning paths that traditional methods miss.
Unified Data Source: LGMs can ingest data from various sources, including HR systems, learning management platforms (LMS), and job descriptions. This creates a centralized skills repository, eliminating data silos and providing a unified view of the workforce’s capabilities.
Continuous Learning: LGMs are constantly learning and evolving. As new skills emerge and existing skill sets change, the skills graph automatically updates to reflect these changes. This ensures that the skills data remains relevant and up-to-date.
Actionable Insights: LGMs provide powerful analytics that can be used to identify skill shortages, predict future skill needs, and measure the effectiveness of training programs. These insights empower companies to make data-driven talent development and workforce planning decisions.
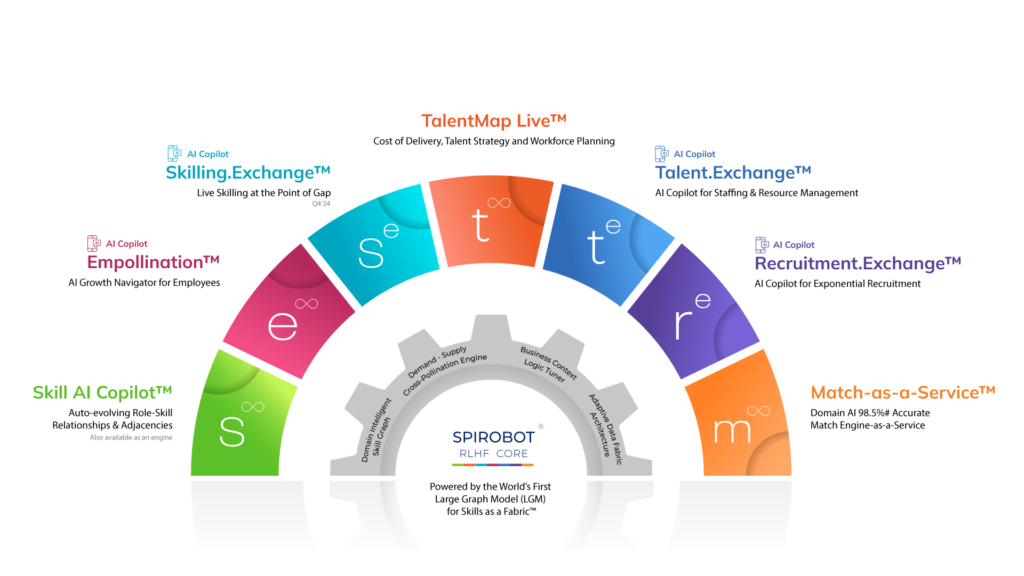
A prime example of the transformative power of LGMs is Spire.AI. This innovative platform leverages the world’s largest LGM for skills to provide companies with a comprehensive solution for skills management. Spire.AI’s LGM goes beyond simply mapping skills; it understands the context and relationships between skills, allowing for a nuanced and insightful analysis of a company’s talent pool.
Spire.AI has developed the world’s first Large Graph Model(LGM) for skills with 10 Million+ Skill Nodes in the LGM built on over 16 years of research.
This vast knowledge base allows for highly accurate and nuanced skill assessments, defined and auto-updating role-skill frameworks, auto-generated employee skill profiles, targeted learning paths, career path simulations, and internal mobility.
By utilizing Spire.AI, companies can better understand their workforce’s capabilities, identify critical skill gaps, and develop targeted training programs to bridge them. This empowers them to build a future-proof workforce that is equipped with the skills needed to succeed in the ever-changing business landscape.
Unlocking the Potential: How LGM Works for Skills
Now that we understand the underlying structure and data sources let’s explore how LGM translates this knowledge into practical applications for organizations.
- Skills Gap Analysis: Identifying the discrepancy between your workforce’s skills and the skills required for success. An LGM for skills or a skill graph can pinpoint critical skills missing from your talent pool and suggest areas for targeted skilling initiatives. Spire.AI Copilot for Talent, with its auto-evolving domain-intelligent LGM-based Role-Skill Framework that acts as a single source of truth for role-skill data, can automatically identify complex skill mixes and skill requirements for every role at the base, enhanced, and expert levels. This allows for a highly targeted skill gap analysis.
- Building Personalized Learning Paths: LGM can recommend the most effective learning paths for individual employees by considering their skill sets and career goals. Spire.AI Copilot for Talent can leverage its vast LGM to suggest relevant courses and create personalized learning journeys that consider an individual’s existing skill foundation, career aspirations, and the organization’s future vision.
An LGM for skills or a skill graph can pinpoint critical skills missing from your talent pool and suggest areas for targeted skilling initiatives.
- Career Path Simulations: Beyond skills gap analysis and talent matching, LGMs unlock a powerful tool for career development: simulating future career paths. By analyzing how skill sets evolve within specific roles, LGMs can map potential career progressions for lateral and vertical growth within the organization, highlighting the skills needed to advance. LGMs can identify hidden connections between skills, suggesting unexpected transitions that leverage transferable abilities. These simulations empower employees and organizations to make informed decisions about skill development and future career journeys.
Spire.AI Copilot for Talent can elevate this process to a whole new level. Powered by the world’s largest LGM for skills, Spire.AI Copilot for Talent leverages its extensive skill graph (with over 10 million skill nodes in LGM) to auto-generate highly sophisticated simulations for every employee in the organization.
- Matching Skills to Roles: When a new position opens up, the LGM can analyze candidate profiles and identify individuals with the most relevant skill sets for the role. This can streamline the recruitment process and ensure a better fit.
- Identifying Skill Adjacencies: LGMs can uncover hidden connections between skills. This can be particularly valuable for identifying individuals with transferable skills that can be leveraged for new roles or projects.
- Future-Proofing Your Workforce: By analyzing industry trends and emerging technologies, LGMs can help organizations identify the skills they’ll need to stay competitive in the future. This allows for proactive skill development initiatives to keep your workforce adaptable and relevant.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Skills with LGMs
Large Graph Models are poised to revolutionize how we manage and develop skills within the workforce. The future of Large Graph Models (LGMs) for skills is nothing short of a talent revolution. Imagine a world where organizations seamlessly transform into skill-based powerhouses.
Gone are the days of rigid job descriptions and one-size-fits-all approaches. LGMs will map hidden connections between skills, enabling talent mobility and fostering a culture of continuous learning.
LGMs will become the ultimate talent architects, weaving intricate tapestries of human potential. Gone are the days of rigid job descriptions and one-size-fits-all approaches. LGMs will map hidden connections between skills, enabling talent mobility and fostering a culture of continuous learning. Think marketing specialists are morphing into data wizards or accountants, blossoming into financial analysts.
This skill fluidity, powered by LGMs, will unlock an era of unprecedented organizational agility and employee empowerment. The future of work is not just about filling roles; it’s about harnessing the boundless potential of a truly skilled workforce.