The traditional approach to managing talent centered around job titles and organizational hierarchies, is increasingly outdated. Organizations must become more agile, adaptable, and responsive to change in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape. This necessitates a shift towards a skills-based approach, where employees are valued and managed based on their competencies rather than their job roles.
At the heart of this transformation lies a powerful technology: Skills-as-a-Fabric. This innovative approach leverages a dynamic, auto-evolving role-skill framework powered by Large Graph Models (LGMs) to create a comprehensive and intelligent understanding of an organization’s talent pool.
The Limitations of Traditional Skill Databases
Traditional skill databases and dictionaries often fail to meet modern organizational needs. These systems typically rely on static lists of skills, making it challenging to capture the nuances and complexities of employee competencies. Additionally, they struggle to identify emerging skills or skill requirements.
Traditional skill databases and dictionaries often fail to meet modern organizational needs.
These systems typically rely on static lists of skills, making it challenging to capture the nuances and complexities of employee competencies.
Organizations need a more sophisticated solution to unlock the potential of a skills-based approach. This solution must adapt to the ever-changing business environment and provide actionable insights into talent development and deployment.
The Power of Skills-as-a-Fabric Technology
Skills-as-a-Fabric technology is a transformational approach that reimagines how organizations view and manage talent. By representing skills as a connected network, or a “fabric,” this technology enables a deeper understanding of how skills relate to each other and how they contribute to organizational goals.
By representing skills as a connected network, or a “fabric,” this technology enables a deeper understanding of how skills relate to each other and how they contribute to organizational goals.
This technology’s core is the large graph model (LGM) for Skills. LGMs are advanced AI models capable of processing and analyzing vast amounts of data, including job descriptions, employee profiles, and external skill information. Organizations can unlock many opportunities for growth, innovation, and agility by shifting the focus from job titles to skills.
A Holistic View of Talent
Unlike traditional systems that silo skills within job descriptions and departments, Skills-as-a-Fabric creates a connected ecosystem where skills are seen as the fundamental building blocks of an organization. This holistic view enables:
A Holistic View of Talent
– Comprehensive Skill Inventory
– Skill Relationship Mapping
– Dynamic Skill Proficiencies
- Comprehensive Skill Inventory: A centralized repository of all skills across the organization, providing a clear picture of the talent pool.
- Skill Relationship Mapping: Understanding how skills connect and complement each other, identifying potential skill combinations for new roles or projects.
- Dynamic Skill Proficiencies: Tracking skill levels to identify skill gaps and development opportunities.
Real-Time Talent Insights
Skills-as-a-Fabric technology empowers organizations with real-time data-driven insights into their talent landscape. This enables:
Real-Time Talent Insights
– Strategic Workforce Planning
– Talent Acquisition Optimization
– Performance Management
– Succession Planning
- Strategic Workforce Planning: Identifying critical skills for future business objectives and aligning talent development strategies accordingly.
- Talent Acquisition Optimization: Sourcing candidates based on specific skill requirements rather than job titles.
- Performance Management: Linking performance evaluations to skill development and career progression.
- Succession Planning: Identifying high-potential employees with the necessary skills for leadership roles.
Driving Innovation and Agility
By fostering a skills-based culture, organizations can become more innovative and agile. Key benefits include:
Driving Innovation and Agility
– Cross-Functional Collaboration
– Rapid Skill Acquisition
– Project-Based Work
– Enhanced Employee Engagement
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Breaking down silos by connecting employees with complementary skills, leading to increased creativity and problem-solving.
- Rapid Skill Acquisition: Identifying and developing emerging skills to stay ahead of industry trends and disruptive technologies.
- Project-Based Work: Assembling teams based on specific project requirements, optimizing resource allocation and project success.
- Enhanced Employee Engagement: Empowering employees to take ownership of their career development by focusing on skill acquisition and growth.
Overcoming Challenges
Implementing a Skills-as-a-Fabric approach requires addressing particular challenges:
- Data Quality and Consistency: Ensuring accurate and up-to-date skill data is essential for practical analysis.
- Skill Framework Development: Creating a standardized skill framework that accurately represents the organization’s skill set.
- Change Management: Overcoming resistance to change and fostering a culture that values skills over job titles.
- Technology Integration: Integrating Skills-as-a-Fabric technology with existing HR systems and business processes.
By carefully addressing these challenges, organizations can harness the power of Skills-as-a-Fabric technology to create a more agile, innovative, and employee-centric workplace.
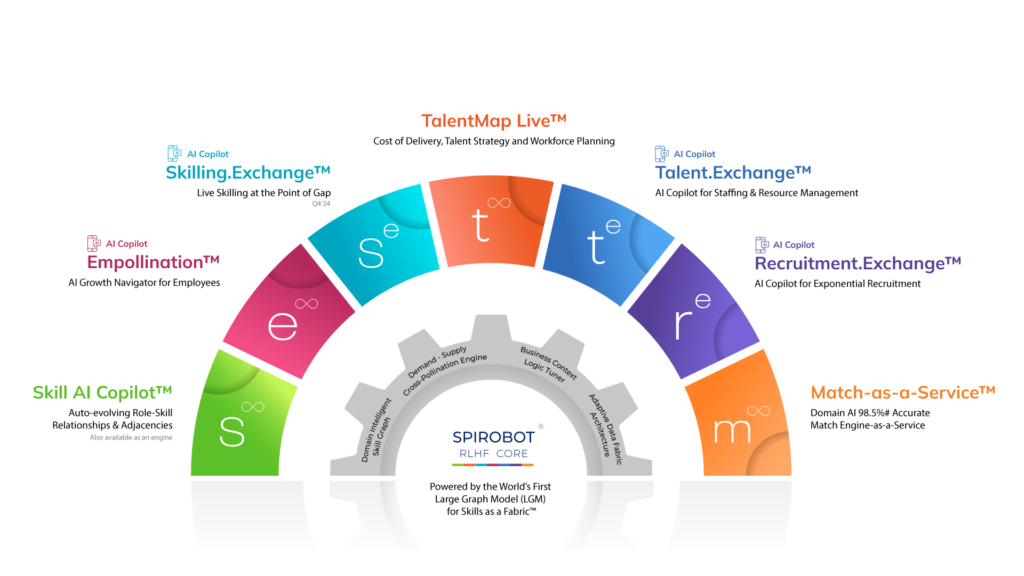
Core Skill Engines: The Indispensable Element
Organizations need a robust core skill engine to transition to a Skills-Based Organization (SBO) successfully. A core skill engine is the beating heart of a Skills-as-a-Fabric platform. The intelligent system underpins the entire approach, transforming raw data into actionable insights and driving strategic decision-making. This engine, powered by LGM technology, is the foundation for a skills-based approach.
A core skill engine is the beating heart of a Skills-as-a-Fabric platform.
The intelligent system underpins the entire approach, transforming raw data into actionable insights and driving strategic decision-making.
This engine, powered by LGM technology, is the foundation for a skills-based approach.
Key Functions of a Core Skill Engine
- Skill Frameworks: Develop a comprehensive and standardized framework for classifying and organizing skills, ensuring consistency and accuracy across the organization.
- Skill Extraction and Profiling: Automatically identifies and extracts skills from various sources, including job descriptions, resumes, performance reviews, and employee-generated data.
- Skill Proficiency Assessment: This method evaluates employee skill levels through various methods, such as assessments, certifications, and performance data.
- Skill Gap Analysis: Identifies organizational skill deficiencies and prioritizes skill development initiatives.
- Skill Matching and Recommendation: Matches employee skills to suitable roles, projects, and development opportunities based on real-time data and predictive analytics.
- Skill Trajectory Modeling: Predicts skill requirements based on business objectives, industry trends, and technological advancements.
- Skill-Based Talent Marketplace: This platform allows employees to showcase their skills and connect with opportunities, fostering internal mobility and collaboration.
Benefits of a Robust Core Skill Engine
- Enhanced Talent Visibility: This feature provides a clear and up-to-date picture of the organization’s talent pool, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Improved Talent Acquisition: Identifies suitable candidates with the necessary skills to fill critical roles efficiently.
- Accelerated Talent Development: Tailors learning and development programs to address specific skill gaps and enhance employee performance.
- Optimized Workforce Planning: Anticipates future skill needs and proactively builds a talent pipeline.
- Increased Organizational Agility: Matches employee skills to Enables rapid response to changing business conditions by leveraging available skills effectively.and predictive analytics.
A well-designed core skill engine is essential for organizations seeking to maximize the potential of their workforce and achieve long-term success. By investing in this critical component, organizations can unlock the full power of a Skills-as-a-Fabric approach and drive significant business outcomes.
Large Graph Models (LGM) for Skills: The Key to Unlocking Potential
LGMs for Skills are the driving force behind the success of a skills-based approach. By leveraging their ability to process and analyze vast amounts of data, LGMs offer several key benefits:
- Personalized Learning Journeys: LGMs can analyze employees’ skill profiles and recommend tailored learning paths to help them develop new competencies. This fosters a culture of continuous learning and development.
- Enhancing Internal Mobility: LGMs can facilitate internal mobility and career progression by matching employee skills with open roles. This helps organizations retain top talent and create a more engaged workforce.
- Optimizing Talent Allocation: LGMs can analyze skill availability and demand to maximize talent allocation across projects and teams. This improves operational efficiency and project success.
Transforming Your Organization with Skills-as-a-Fabric Technology
Adopting a skills-based approach powered by Skills-as-a-Fabric technology can profoundly impact your organization. By focusing on employee competencies, you can:
- Increase agility and adaptability: A skills-based approach enables organizations to respond to market or business environment changes quickly.
- Enhance innovation: By fostering a culture of learning and development, organizations can encourage employees to explore new ideas and take on challenging projects.
- Improve employee engagement and retention: Employees who feel valued for their skills and have opportunities to grow and develop are more likely to be engaged and committed to the organization.
- Optimize resource allocation: By matching skills with projects and teams, organizations can maximize the utilization of their talent pool.
Industry Leadership: Spire.AI and the Skills-as-a-Fabric Revolution
While the concept of Skills-as-a-Fabric technology is gaining traction, there’s a clear frontrunner in bringing this vision to life: Spire.AI.
Spire.AI stands out as the pioneering force behind Skills-as-a-Fabric technology. Their innovative platform, powered by cutting-edge Large Graph Models (LGMs), empowers organizations to create a dynamic and intelligent skills ecosystem.
Here’s what sets Spire.AI apart:
- Advanced LGM Technology: Spire.AI leverages the power of the world’s first and largest LGM to unlock the full potential of skill data, providing a deeper understanding of role-skill relationships and requirements.
- Comprehensive Skill Framework: Spire.AI offers a robust skill framework that can be customized to specific industry needs, ensuring accurate and consistent skill classification.
- Holistic Talent Management: Spire.AI integrates seamlessly with existing HR systems, providing a centralized platform for managing all talent development and deployment aspects.
- Proven Success: Spire.AI has a proven track record of helping leading organizations achieve significant results through a skills-based approach.
By partnering with Spire.AI, organizations have gained a powerful ally in their journey toward becoming a sustainable and agile Skill-Based Organization. With its cutting-edge technology and deep expertise, Spire.AI is helping businesses unlock the full potential of their workforce and thrive in the dynamic business landscape.
Conclusion
Transitioning to a skills-based organization is a complex journey, but the rewards are significant. By embracing Skills-as-a-Fabric technology and skills modeling over competency modeling, and leveraging the power of Large Graph Models, organizations can unlock the full potential of their workforce and achieve sustainable success in the digital age.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the skill-based approach?
A skills-based approach focuses on developing and utilizing employees’ skills to drive business outcomes. It emphasizes continuous learning, skill development, and talent optimization.
What is Skills-as-a-Fabric technology?
Skills-as-a-Fabric technology is a transformational approach that reimagines how organizations view and manage talent; by representing skills as a connected network, or a “fabric,” this technology enables a deeper understanding of how skills relate to each other and how they contribute to organizational goals.